Healthy vs. Unhealthy Gums
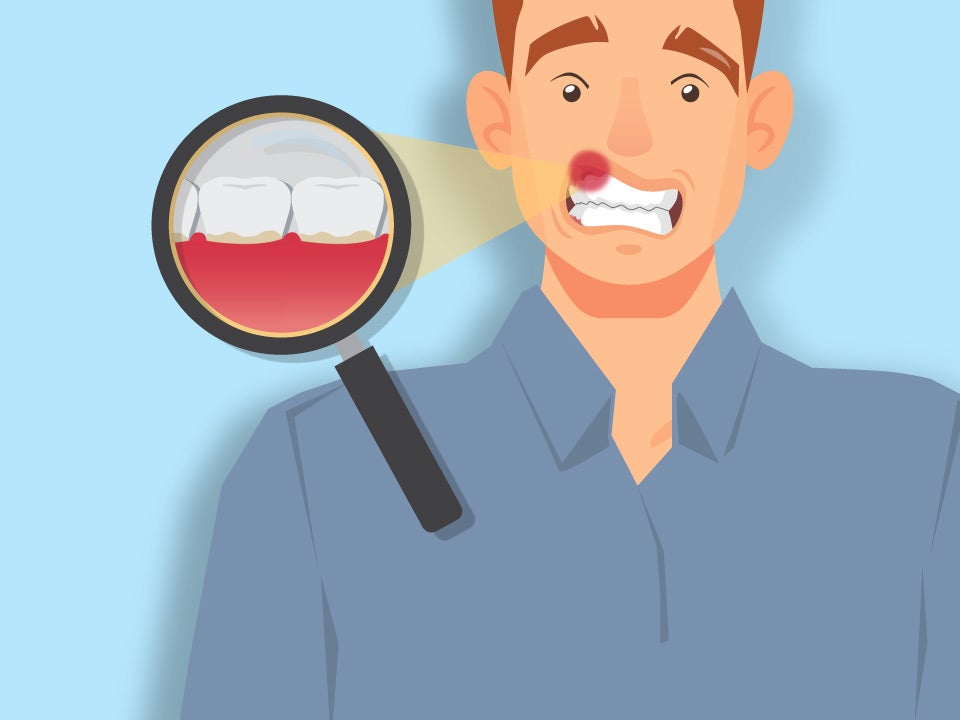
Start by looking at your gums if you think you might have an issue with gum disease. Healthy gums will look firm and pink. Unhealthy gums will look red or swollen. They also might bleed when you brush or floss.
Bleeding Gums
How Do I Take Care of My Gums?
Taking care of your gums is just as important as taking care of your teeth. Here are some ways how to get healthy gums.
Brushing and Flossing
Fluoride Toothpaste
Use a gum care toothpaste that contains fluoride. Fluoride keeps enamel – the hard surface that protects your teeth – strong and resistant to tooth decay. Make sure that the toothpaste you use has the American Dental Association (ADA) seal of approval.
Rinse with Mouthwash
Schedule Dental Checkups
Your dentist can check your gums for any signs of gum disease while also professionally cleaning your teeth. A teeth cleaning by your dentist is the only way to remove tartar. It will also eliminate any remaining plaque you missed brushing and flossing.
Stop Smoking
Smoking has been proven to cause numerous health issues, including weakening the body’s immune system. Damaged gums on a smoker also have a difficult time in healing. Additionally, gum disease treatment options aren’t as successful in people who smoke.
Eat Healthy Foods
Food consumption is a way to naturally keep your gums healthy. Avoid eating or drinking foods that are high in sugar and starches. Those foods and drinks produce acids that remain in the mouth.

What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is when the gumline becomes inflamed enough to affect the bones that contain and support your teeth. There are three stages to gum disease: gingivitis, periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis.
Gingivitis
This is the first stage of gum disease. The gums become inflamed due to plaque collecting along the gumline. They’ll appear to be swollen or red. The gums can also bleed when you brush or floss. Gingivitis can still be reversed as the infection has yet to reach the bone.
Periodontitis
Advanced Periodontitis
Gum Disease Causes
Bacteria in plaque cause gum disease. Plaque is a clear, sticky film that constantly forms on teeth. Tartar, also known as calculus, forms when plaque isn’t removed and hardens on a tooth’s surface. Only a dental professional can remove tartar. Brushing and flossing alone won’t remove it.
Dry mouth is another possible cause of gum disease. Antihistamines, decongestants, and painkillers can cause dry mouth.
Gum Disease Symptoms
- Gums that are red, swollen, or tender
- Signs of gum recession
- Brushing and flossing cause your gums to bleed
- Chronic bad breath
- Severe tooth sensitivity to foods or drinks that are hot or cold
- Loose teeth
- Painful when chewing food
- Realigned bite
- Dentures no longer fit correctly
- Visible puss emanating from teeth and gums

Gum Disease Treatment Options
Gingivitis can be reversed by learning how to improve gum health with a good oral care routine. Gum disease that has advanced to phases two or three, periodontitis or advanced periodontitis, requires a dental treatment option. Here are some ways to fix gum damage due to periodontitis or advanced periodontitis.
Scaling and Root Planing
This two-step procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from a tooth’s surface and below the gumline. Removal can occur with a manual hand device or an ultrasonic scaling device.
Root planing involves smoothing out a root’s surface to make rough areas smooth. This process decreases gum inflammation and prevents plaque and tartar from re-adhering to the root’s surface.
Gingivectomy
A gingivectomy is the complete removal of a portion of gum in and around a tooth to treat gum disease. The process also lengthens the height or width of a tooth.
Pocket Reduction Surgery
Also called flap surgery, this treatment involves tiny incisions in the gums to lift the tissue back to expose the root. Your dentist can then perform more effective scaling and root planing. The underlying bone might need to be recontoured if the advanced periodontitis has caused bone loss.
Tooth Extraction
There are several types of extractions, the two most common are: simple and surgical.
What Is a Gum Stimulator?
A gum stimulator is a dental tool that has a long, metal arm and a rubber or silicone tip. Dentists recommend them to patients who have gum disease. Implementing a gum stimulator can prevent gum disease from spreading.
How to Use a Gum Stimulator
Find a Dentist Near You to Discuss Your Dental Hygiene
Consult your dentist to discuss the best methods to keep your gums healthy or if you have symptoms of gum disease. Or if you're looking for a dentist and are wondering where you can find a dentist near me. Visit The Smile Generation to find a dentist near you for your gum disease prevention and treatment needs. You can read patient reviews, peruse staff bios, and schedule an appointment online with a click of your mouse.
Find your trusted, local dentist today!
Sources
- Crest. (n.d.). Gum disease pictures: What do healthy gums look like? Crest. Retrieved from https://crest.com/en-us/oral-care-tips/gum-health/gum-disease-pictures-what-do-healthy-gums-look-like
- Healthline. (2022, June 28). Ways to keep gums healthy. Healthline. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/ways-to-keep-gums-healthy
- MouthHealthy. (n.d.). Fluoride: Topical and systemic benefits. American Dental Association. Retrieved from https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/f/fluoride#:~:text=Before%20teeth%20break%20through%20the%20gums%2C%20the%20fluoride,benefit.%20After%20teeth%20erupt%2C%20fluoride%20helps%20rebuild%20%28remineralize%29
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, April 12). Periodontal (gum) disease. CDC. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/diseases/periodontal-gum-disease.html
- WebMD. (n.d.). Teeth and gum care. WebMD. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/teeth-and-gum-care
- Colgate. (n.d.). What you need to know about gum disease. Colgate. Retrieved from https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/gum-disease/what-you-need-to-know-about-gum-disease
- Colgate. (n.d.). What dentists do when root planing and scaling teeth. Colgate. Retrieved from https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/gum-disease/what-dentists-do-when-root-planing-and-scaling-teeth
- Colgate. (n.d.). Gingivectomy surgery: What you need to know. Colgate. Retrieved from https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/gum-disease/gingivectomy-surgery-what-you-need-to-know
- Mayo Clinic. (2023, May 9). Periodontitis: Diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/periodontitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354479
- Colgate. (n.d.). Tooth extraction. Colgate. Retrieved from https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/tooth-removal/tooth-extraction
- Colgate. (n.d.). Gum stimulator: What is it and how do I use it? Colgate. Retrieved from https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/adult-oral-care/gum-stimulator-what-is-it-and-how-do-i-use-it
Smile Generation blog articles are reviewed by a licensed dental professional before publishing. However, we present this information for educational purposes only with the intent to promote readers’ understanding of oral health and oral healthcare treatment options and technology. We do not intend for our blog content to substitute for professional dental care and clinical advice, diagnosis, or treatment planning provided by a licensed dental professional. Smile Generation always recommends seeking the advice of a dentist, physician, or other licensed healthcare professional for a dental or medical condition or treatment.